Cognito and API Gateway
Cognito authorizers provide a fully managed access control integration with API Gateway, as illustrated in Figure 4-5. API consumers exchange their credentials (a client ID and secret) for access tokens via a Cognito endpoint. These access tokens are then included with API requests and validated via the Cognito authorizer.
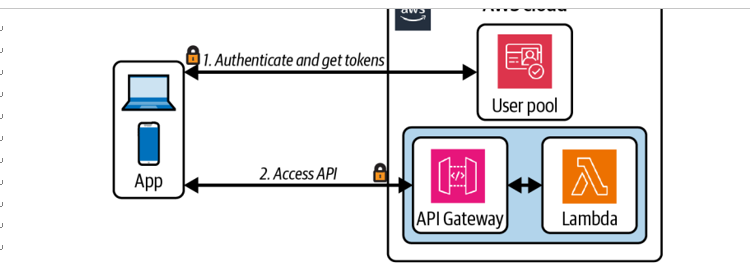
Figure 4-5. API Gateway Cognito authorizer
Additionally, an API endpoint can be assigned a scope. When authorizing a request to the endpoint, the Cognito authorizer will verify the endpoint’s scope is included in the client’s list of permitted scopes.
Securing HTTP APIs
If you are using an API Gateway HTTP API, rather than a REST API, you will not be able to use the native Cognito authorizer. Instead, you have a few alternative options. We’ll explore examples of the most convenient two: Lambda authorizers and JWT authorizers.
JWT authorizers can also be used to authenticate API requests with Amazon Cognito when using HTTP APIs.
JWT authorizers
If your authorization strategy simply involves a client submitting a JSON Web Token for verification, using a JWT authorizer will be a good option. When you use a JWT authorizer, the whole authorization process is managed by the API Gateway service.
JWT is an open standard that defines a compact, self-contained way of securely transmitting information between parties as JSON objects. JWTs can be used to ensure the integrity of a message and the authentication of both the message producer and consumer.
JWTs can be cryptographically signed and encrypted, enabling ver‐ ification of the integrity of the claims contained within the token while keeping those claims hidden from other parties.
You first configure the JWT authorizer and then attach it to a route. The Cloud‐
Formation resource will look something like this:
{
“Type” : “AWS::ApiGatewayV2::Authorizer”,
“Properties” : {
“ApiId” : “ApiGatewayId”,
“AuthorizerType” : “JWT”,
“IdentitySource” : [ “$request.header.Authorization” ],
“JwtConfiguration” : {
“Audience” : [ “https://my-application.com” ],
“Issuer” : “https://cognito-idp.us-east-1.amazonaws.com/userPoolID”
},
“Name” : “my-authorizer”
}
}
The IdentitySource should match the location of the JWT provided by the cli‐ ent in the API request; for example, the Authorization HTTP header. The Jwt Configuration should correspond to the expected values in the tokens that will be submitted by clients, where the Audience is the HTTP address for the recipient of the token (usually your API Gateway domain) and the Issuer is the HTTP address for the service responsible for issuing tokens, such as Cognito or Okta.
